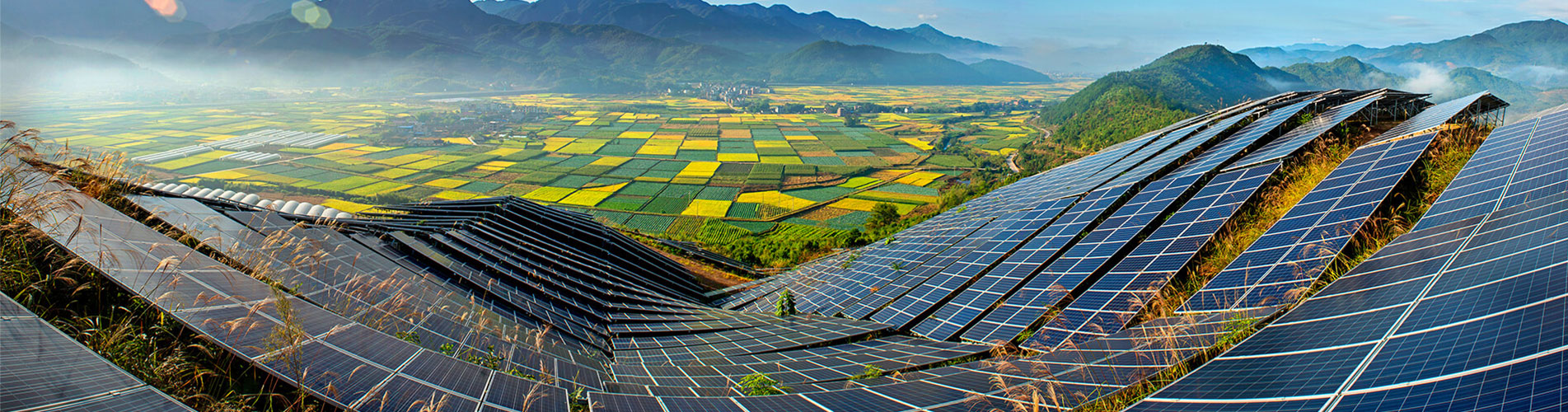
In the pursuit of clean and renewable energy solutions, solar photovoltaic (PV) and solar thermal technologies shine brightly, each with its unique characteristics and distinct applications. While both originate from the same source, they exhibit key differences in functionality, efficiency, and benefits. This article concisely compares their essential distinctions, aiming to provide readers with a clearer understanding and assist in selecting the most suitable solar utilization method.
Definitions
---Solar Photovoltaics (PV):
Solar Photovoltaics is a technology that harnesses the photovoltaic effect to convert sunlight directly into electricity. The core component of a PV system is the photovoltaic cell, which absorbs sunlight and generates an electric current, powering electrical devices or feeding into the grid.
---Solar Thermal:
Solar Thermal, also known as Concentrating Solar Power (CSP), involves using mirrors to concentrate sunlight onto a focal point, heating a working fluid (such as water or molten salt), producing high-temperature, high-pressure steam that drives a turbine to generate electricity.
Differences
Solar Photovoltaics
Solar Thermal
Power Generation Principle
Converts sunlight directly into electricity via the photovoltaic effect
Converts concentrated sunlight into heat, then heat into steam to drive a turbine
Energy Storage
Primarily relies on batteries for excess energy, which can be costly
Can store thermal energy directly (e.g., high-temperature molten salt), making storage cost-effective
Equipment Complexity
Relatively simple, with straightforward installation and maintenance
Complex, requiring high-temperature, high-pressure equipment
Suitability
Ideal for decentralized use, like homes, neighborhoods, and integration with buildings
Suitable for large-scale development, requiring vast land areas and optimal sunlight conditions
Environmental Impact
Zero emissions, environmentally friendly
Similarly, zero emissions and environmentally benign
Pros & Cons
---Solar Photovoltaics:
Pros:
-Abundant resource, virtually inexhaustible.
-Environmentally friendly, with zero emissions during operation.
-Flexible installation, scalable to meet varying demands.
-Simple maintenance, reliable operation, and long lifespan.
-Can be integrated with buildings, conserving land resources.
Cons:
-Low energy density, requiring large areas.
-Relatively low conversion efficiency (around 15%-20% for crystalline silicon PV cells).
-Intermittent operation, dependent on weather and sunlight intensity.
-High initial investment costs, particularly for high-quality PV cells.
---Solar Thermal:
Pros:
-Higher power generation efficiency, potentially reaching 20%-30%.
-Flexible energy storage options, including long-duration storage with molten salt.
-Operational in low temperatures and harsh climates.
Cons:
-High initial investment costs due to complex and expensive equipment.
-Stringent site requirements, necessitating vast land and optimal sunlight.
-Higher operational costs, involving regular inspections and maintenance.
Applications
---Solar Photovoltaics:
Residential rooftop systems, reducing electricity bills.
Large-scale ground-mounted power plants, contributing to grid stability.
Public facilities, such as solar-powered streetlights and advertising billboards.
Portable solar chargers for outdoor activities and emergencies.
Photovoltaic carports, providing shade and generating electricity.
---Solar Thermal:
Solar water heaters, fulfilling domestic hot water needs.
Solar heating systems for building warmth in cold climates.
Industrial steam generation for various industrial processes.
Concentrated Solar Power plants, supplying grid-scale electricity in sunny regions.
Future Prospects
---Solar Photovoltaics:
With continued technological advancements and cost reductions, the future of solar PV looks promising. More countries and regions are embracing PV technologies, driving widespread adoption across households, industries, and transportation sectors. Solar PV is poised to become a key driver in the energy transition towards a greener future.
---Solar Thermal:
Despite initial investment challenges and equipment complexity, Solar Thermal holds significant potential, particularly in its energy storage capabilities. With policy support and technological improvements, CSP could play a crucial role in providing reliable power to remote locations, islands, and other areas requiring continuous supply. Additionally, Solar Thermal's applications in heating, cooling, and industrial processes are expected to expand and deepen.
In summary, solar photovoltaic and solar thermal technologies both harness the power of the sun but differ in their applications and benefits.We hope you found this article helpful, and feel free to contact us if you want to know more.
HQ Mount located in Xiamen, China, is specialized in researching and developing, manufacturing, selling solar mounting system solutions. Our products mainly include solar balcony mount, roof mount, grounding mount, solar carport, solar farm and all mounting accessories.
CONTACT US---XIAMEN HQ MOUNT TECH CO.,LTD
Whatsapp : 18030160771
Tel : 86 05926252889
Email : allie@hqmount.com
 86 05926252889
86 05926252889 allie@hqmount.com
allie@hqmount.com